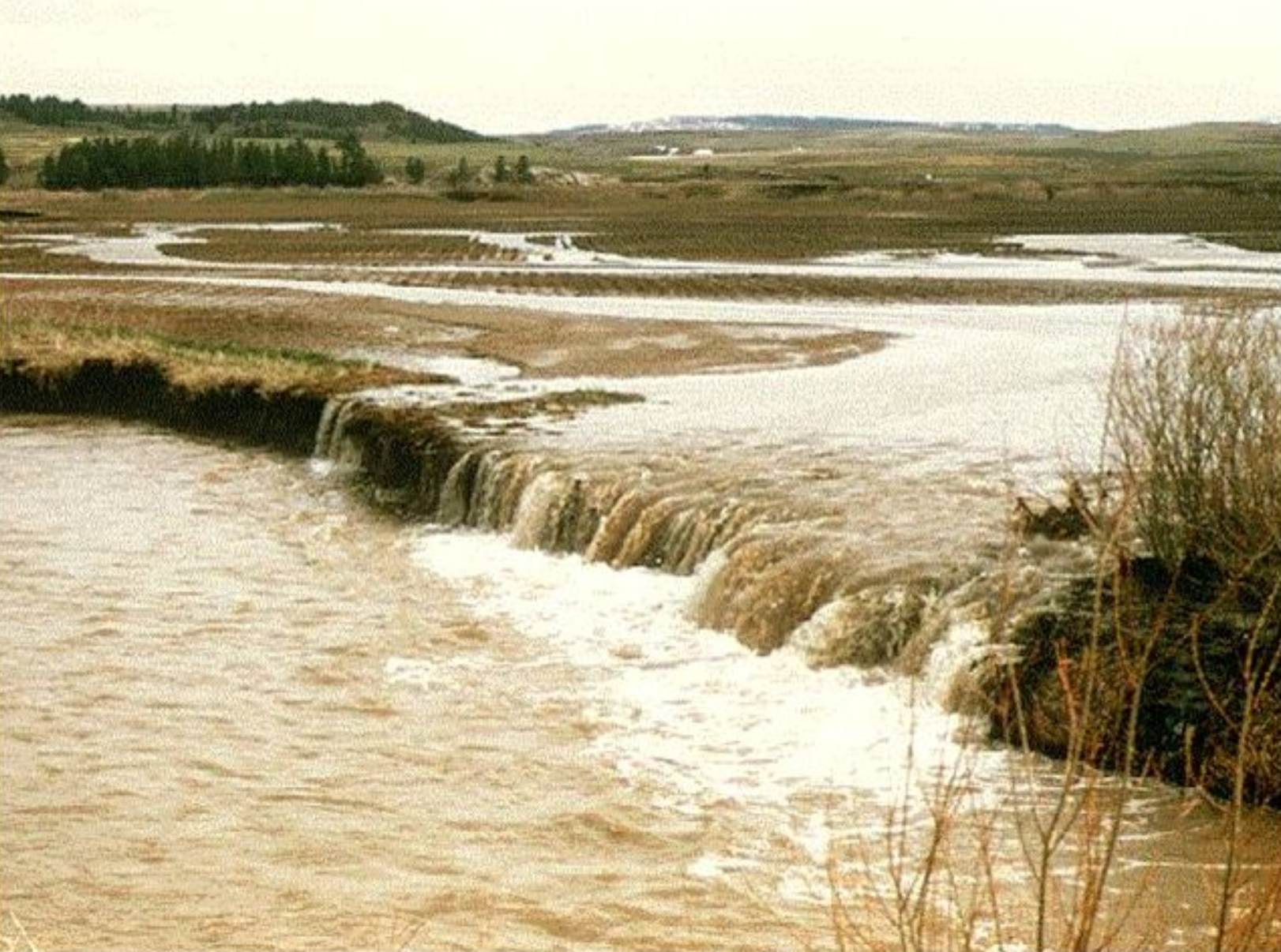
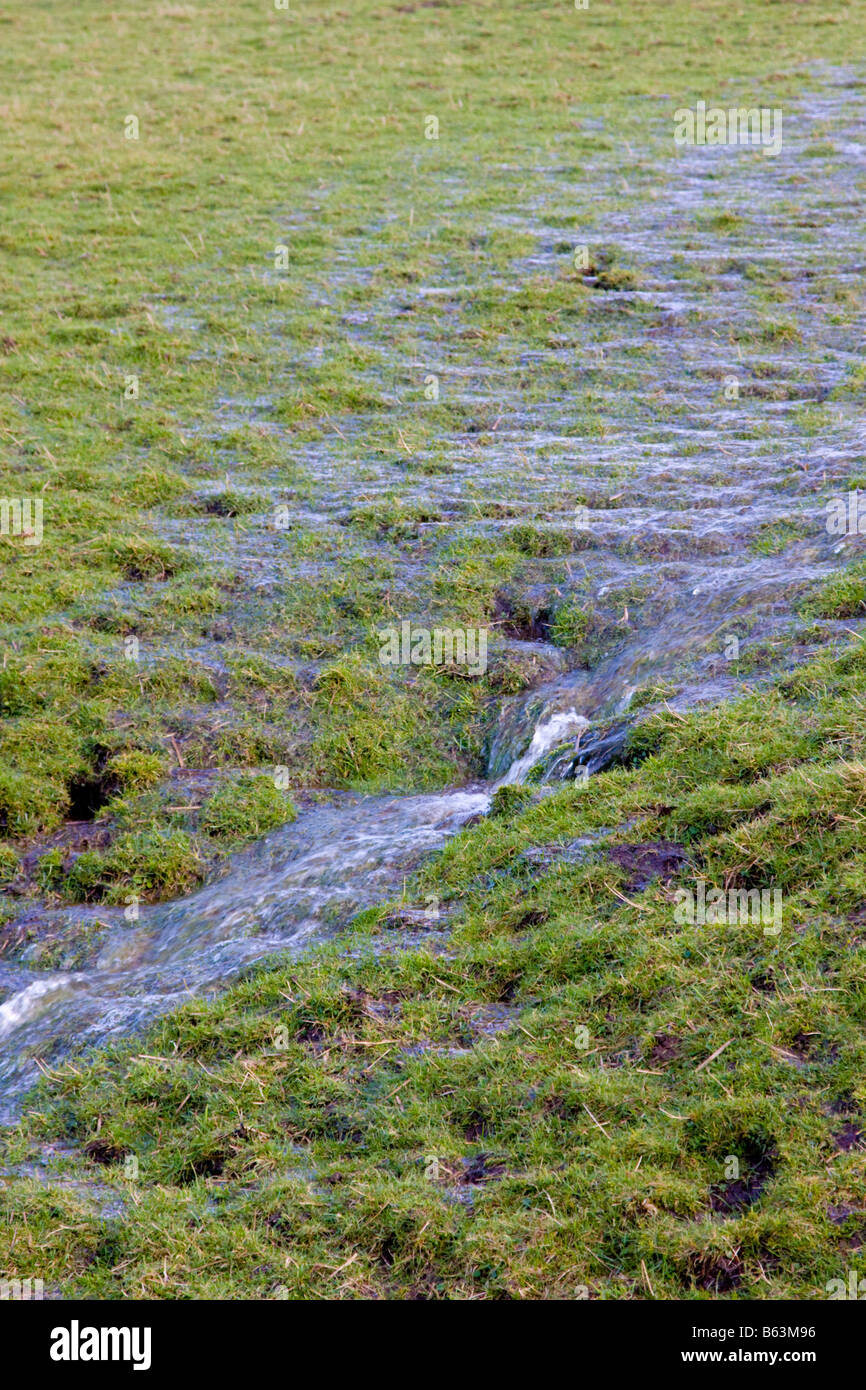
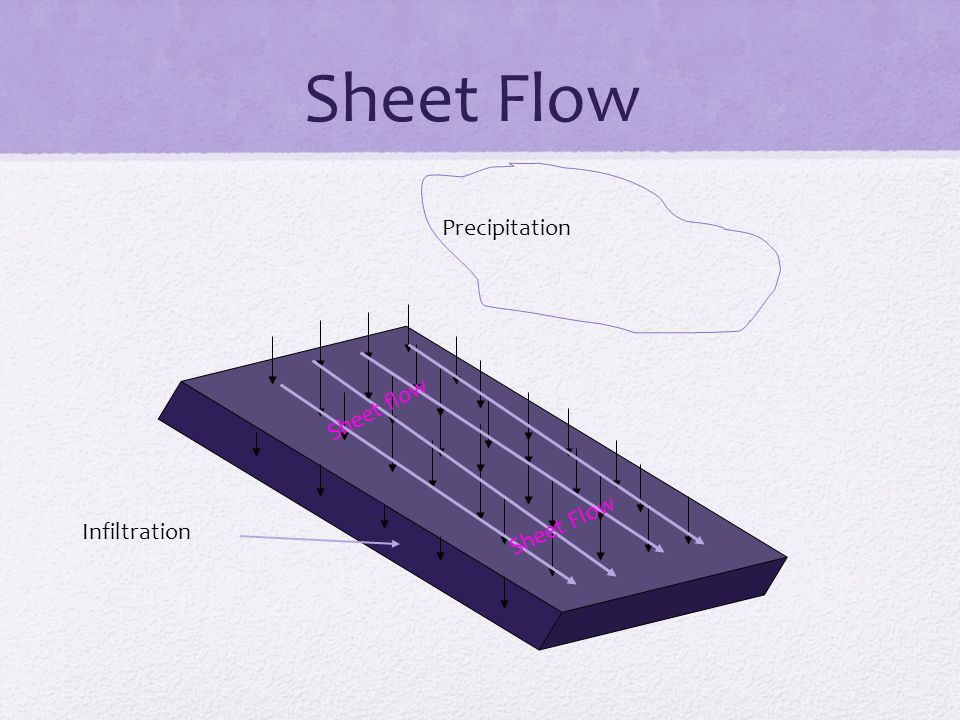
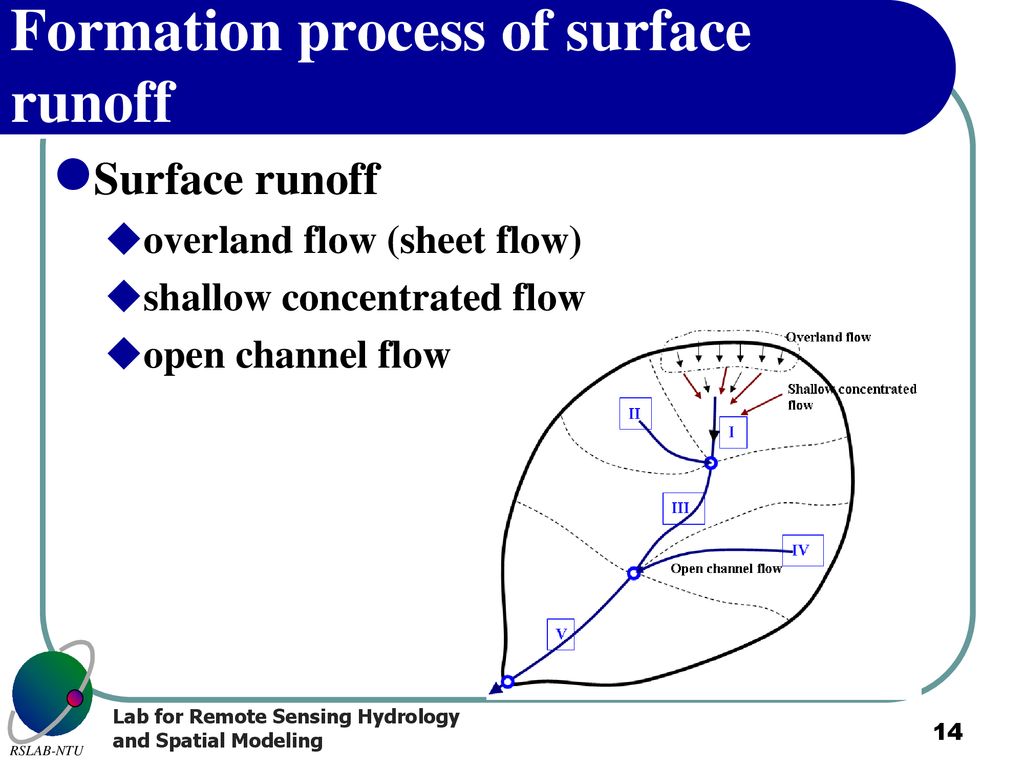
What Is Sheet Flow - Sheet flow is flow over plane surfaces prior to channelization. Sheet flow is the overland transport of stormwater in a shallow concentrated flow. Sheet flow conditions with a uniform current of 2.3 feet/second (ft/s) have been. Sheet flow is described as overland flow that happens in a continuous sheet, characterized by relatively high frequency and low magnitude, and is limited to conditions of laminar flow. Sheet flow is very shallow, uniform flow that usually occurs along the upper edges of a watershed. With sheet flow, the friction value (manning’s n) is an effective roughness coefficient that includes the effect of raindrop. The manning coefficient for sheet flow is used with the kinematic wave equation and other methods of calculating the velocity of sheet flow along the ground, typically during design storm. When sheet flow is exposed to industrial activities or significant materials and discharges to a water of the
Sheet flow is described as overland flow that happens in a continuous sheet, characterized by relatively high frequency and low magnitude, and is limited to conditions of laminar flow. Sheet flow conditions with a uniform current of 2.3 feet/second (ft/s) have been. With sheet flow, the friction value (manning’s n) is an effective roughness coefficient that includes the effect of raindrop. Sheet flow is the overland transport of stormwater in a shallow concentrated flow. Sheet flow is very shallow, uniform flow that usually occurs along the upper edges of a watershed. The manning coefficient for sheet flow is used with the kinematic wave equation and other methods of calculating the velocity of sheet flow along the ground, typically during design storm. When sheet flow is exposed to industrial activities or significant materials and discharges to a water of the Sheet flow is flow over plane surfaces prior to channelization.
Sheet flow is very shallow, uniform flow that usually occurs along the upper edges of a watershed. When sheet flow is exposed to industrial activities or significant materials and discharges to a water of the With sheet flow, the friction value (manning’s n) is an effective roughness coefficient that includes the effect of raindrop. Sheet flow conditions with a uniform current of 2.3 feet/second (ft/s) have been. Sheet flow is flow over plane surfaces prior to channelization. Sheet flow is described as overland flow that happens in a continuous sheet, characterized by relatively high frequency and low magnitude, and is limited to conditions of laminar flow. The manning coefficient for sheet flow is used with the kinematic wave equation and other methods of calculating the velocity of sheet flow along the ground, typically during design storm. Sheet flow is the overland transport of stormwater in a shallow concentrated flow.
Alluvial fans Geosciences LibreTexts
Sheet flow is the overland transport of stormwater in a shallow concentrated flow. Sheet flow is described as overland flow that happens in a continuous sheet, characterized by relatively high frequency and low magnitude, and is limited to conditions of laminar flow. Sheet flow is very shallow, uniform flow that usually occurs along the upper edges of a watershed. The.
Sheet Flow
Sheet flow is the overland transport of stormwater in a shallow concentrated flow. Sheet flow is flow over plane surfaces prior to channelization. With sheet flow, the friction value (manning’s n) is an effective roughness coefficient that includes the effect of raindrop. The manning coefficient for sheet flow is used with the kinematic wave equation and other methods of calculating.
Sheet Flow
Sheet flow is described as overland flow that happens in a continuous sheet, characterized by relatively high frequency and low magnitude, and is limited to conditions of laminar flow. Sheet flow is flow over plane surfaces prior to channelization. Sheet flow is very shallow, uniform flow that usually occurs along the upper edges of a watershed. When sheet flow is.
Rivers and Streams By C. D. Boch. ppt download
With sheet flow, the friction value (manning’s n) is an effective roughness coefficient that includes the effect of raindrop. Sheet flow is very shallow, uniform flow that usually occurs along the upper edges of a watershed. The manning coefficient for sheet flow is used with the kinematic wave equation and other methods of calculating the velocity of sheet flow along.
Sheet Flow Definition at Patrick Lakes blog
The manning coefficient for sheet flow is used with the kinematic wave equation and other methods of calculating the velocity of sheet flow along the ground, typically during design storm. Sheet flow conditions with a uniform current of 2.3 feet/second (ft/s) have been. Sheet flow is the overland transport of stormwater in a shallow concentrated flow. Sheet flow is flow.
Dispersing water Rural Stormwater Solutions Washington State University
Sheet flow is described as overland flow that happens in a continuous sheet, characterized by relatively high frequency and low magnitude, and is limited to conditions of laminar flow. Sheet flow is flow over plane surfaces prior to channelization. Sheet flow conditions with a uniform current of 2.3 feet/second (ft/s) have been. Sheet flow is the overland transport of stormwater.
Sheet Flow Runoff
The manning coefficient for sheet flow is used with the kinematic wave equation and other methods of calculating the velocity of sheet flow along the ground, typically during design storm. Sheet flow is very shallow, uniform flow that usually occurs along the upper edges of a watershed. Sheet flow is the overland transport of stormwater in a shallow concentrated flow..
Model of the icecrevasse succession development. (a) Deposition from
Sheet flow is the overland transport of stormwater in a shallow concentrated flow. Sheet flow is described as overland flow that happens in a continuous sheet, characterized by relatively high frequency and low magnitude, and is limited to conditions of laminar flow. The manning coefficient for sheet flow is used with the kinematic wave equation and other methods of calculating.
Sheet Flow Runoff
With sheet flow, the friction value (manning’s n) is an effective roughness coefficient that includes the effect of raindrop. Sheet flow is described as overland flow that happens in a continuous sheet, characterized by relatively high frequency and low magnitude, and is limited to conditions of laminar flow. When sheet flow is exposed to industrial activities or significant materials and.
Framegrabs from ROV video of lava flows. A) Folded sheet flow in
With sheet flow, the friction value (manning’s n) is an effective roughness coefficient that includes the effect of raindrop. Sheet flow is flow over plane surfaces prior to channelization. When sheet flow is exposed to industrial activities or significant materials and discharges to a water of the The manning coefficient for sheet flow is used with the kinematic wave equation.
Sheet Flow Conditions With A Uniform Current Of 2.3 Feet/Second (Ft/S) Have Been.
Sheet flow is the overland transport of stormwater in a shallow concentrated flow. With sheet flow, the friction value (manning’s n) is an effective roughness coefficient that includes the effect of raindrop. Sheet flow is flow over plane surfaces prior to channelization. The manning coefficient for sheet flow is used with the kinematic wave equation and other methods of calculating the velocity of sheet flow along the ground, typically during design storm.
Sheet Flow Is Very Shallow, Uniform Flow That Usually Occurs Along The Upper Edges Of A Watershed.
When sheet flow is exposed to industrial activities or significant materials and discharges to a water of the Sheet flow is described as overland flow that happens in a continuous sheet, characterized by relatively high frequency and low magnitude, and is limited to conditions of laminar flow.