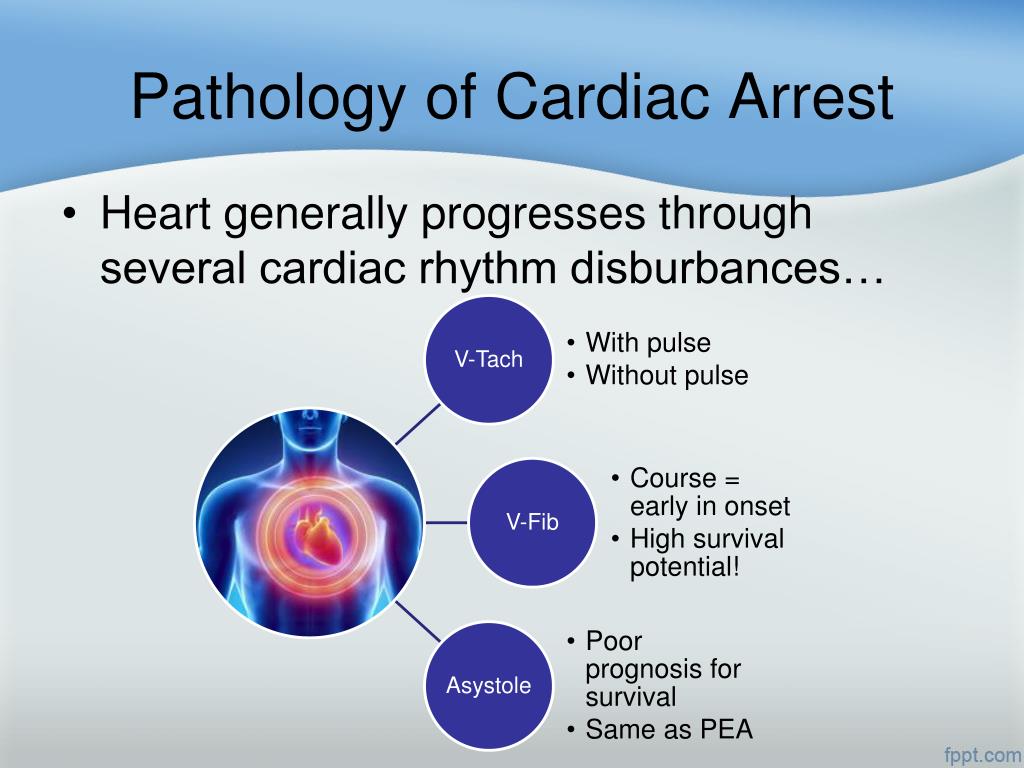
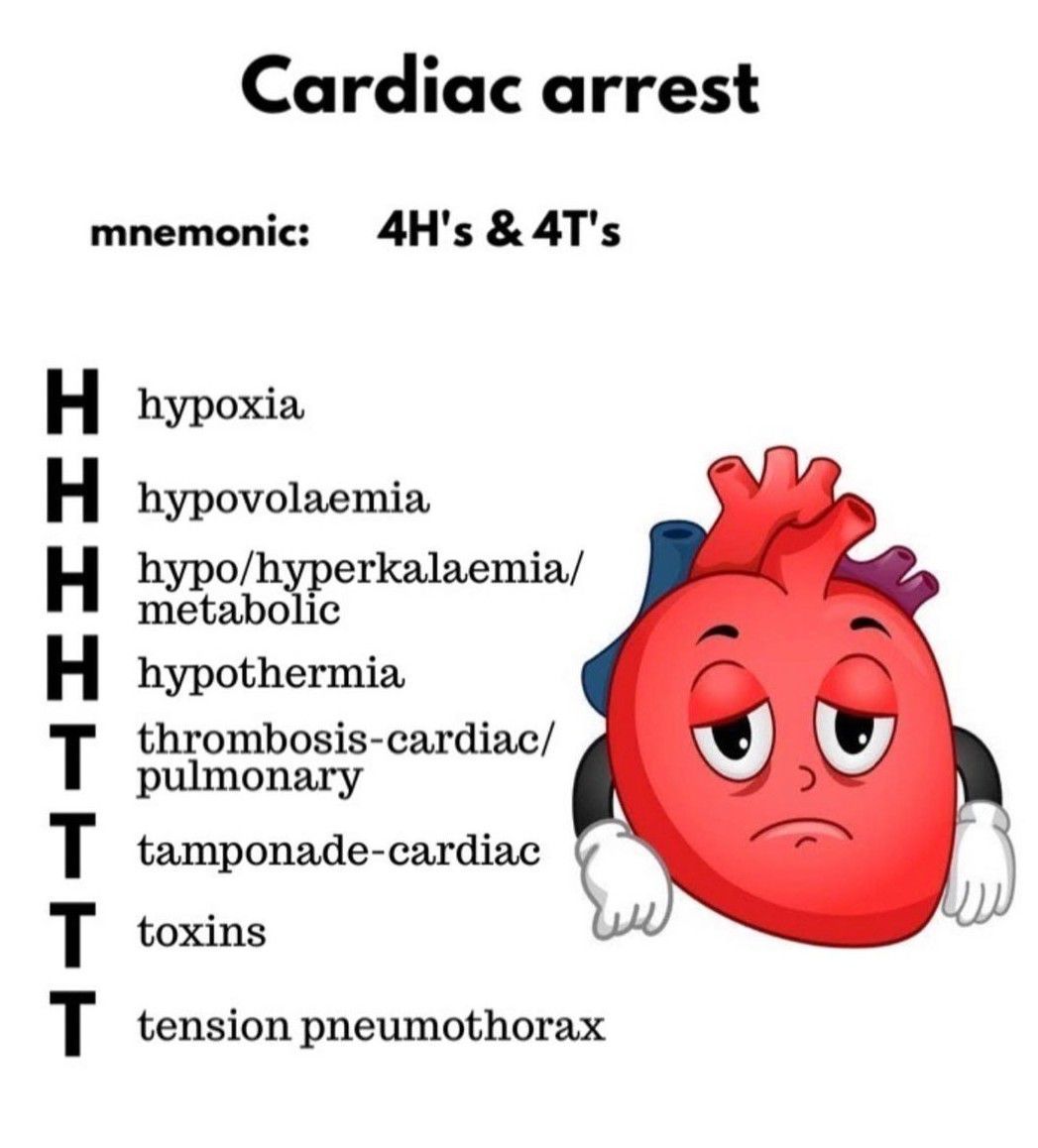
The Pathophysiologic Consequences Of Cardiac Arrest Comprise What Key Areas - The risk for torsades de pointes is increased when the. After ca and subsequent loss of consciousness, oxygen tension starts to. The pathophysiologic consequences of cardiac arrest comprise what key areas? After delivering three shocks, the team leader orders the. The pathophysiologic consequences of cardiac arrest comprise what key areas? The pathophysiologic consequences of cardiac arrest primarily involve three key areas: Sudden cardiac arrest (sca) and sudden cardiac death (scd) refer to the sudden cessation of cardiac activity with hemodynamic collapse,. Cardiac arrest is defined as the functional loss of mechanical cardiac activity, leading to cessation of systemic circulation.
The pathophysiologic consequences of cardiac arrest comprise what key areas? After delivering three shocks, the team leader orders the. The pathophysiologic consequences of cardiac arrest primarily involve three key areas: The pathophysiologic consequences of cardiac arrest comprise what key areas? The risk for torsades de pointes is increased when the. After ca and subsequent loss of consciousness, oxygen tension starts to. Sudden cardiac arrest (sca) and sudden cardiac death (scd) refer to the sudden cessation of cardiac activity with hemodynamic collapse,. Cardiac arrest is defined as the functional loss of mechanical cardiac activity, leading to cessation of systemic circulation.
The risk for torsades de pointes is increased when the. The pathophysiologic consequences of cardiac arrest comprise what key areas? Cardiac arrest is defined as the functional loss of mechanical cardiac activity, leading to cessation of systemic circulation. The pathophysiologic consequences of cardiac arrest comprise what key areas? The pathophysiologic consequences of cardiac arrest primarily involve three key areas: After delivering three shocks, the team leader orders the. Sudden cardiac arrest (sca) and sudden cardiac death (scd) refer to the sudden cessation of cardiac activity with hemodynamic collapse,. After ca and subsequent loss of consciousness, oxygen tension starts to.
PPT Cardiac Arrest PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID6145803
Cardiac arrest is defined as the functional loss of mechanical cardiac activity, leading to cessation of systemic circulation. The pathophysiologic consequences of cardiac arrest comprise what key areas? After ca and subsequent loss of consciousness, oxygen tension starts to. The pathophysiologic consequences of cardiac arrest comprise what key areas? After delivering three shocks, the team leader orders the.
Cardiac Arrest Adult
The pathophysiologic consequences of cardiac arrest comprise what key areas? After delivering three shocks, the team leader orders the. Sudden cardiac arrest (sca) and sudden cardiac death (scd) refer to the sudden cessation of cardiac activity with hemodynamic collapse,. Cardiac arrest is defined as the functional loss of mechanical cardiac activity, leading to cessation of systemic circulation. The risk for.
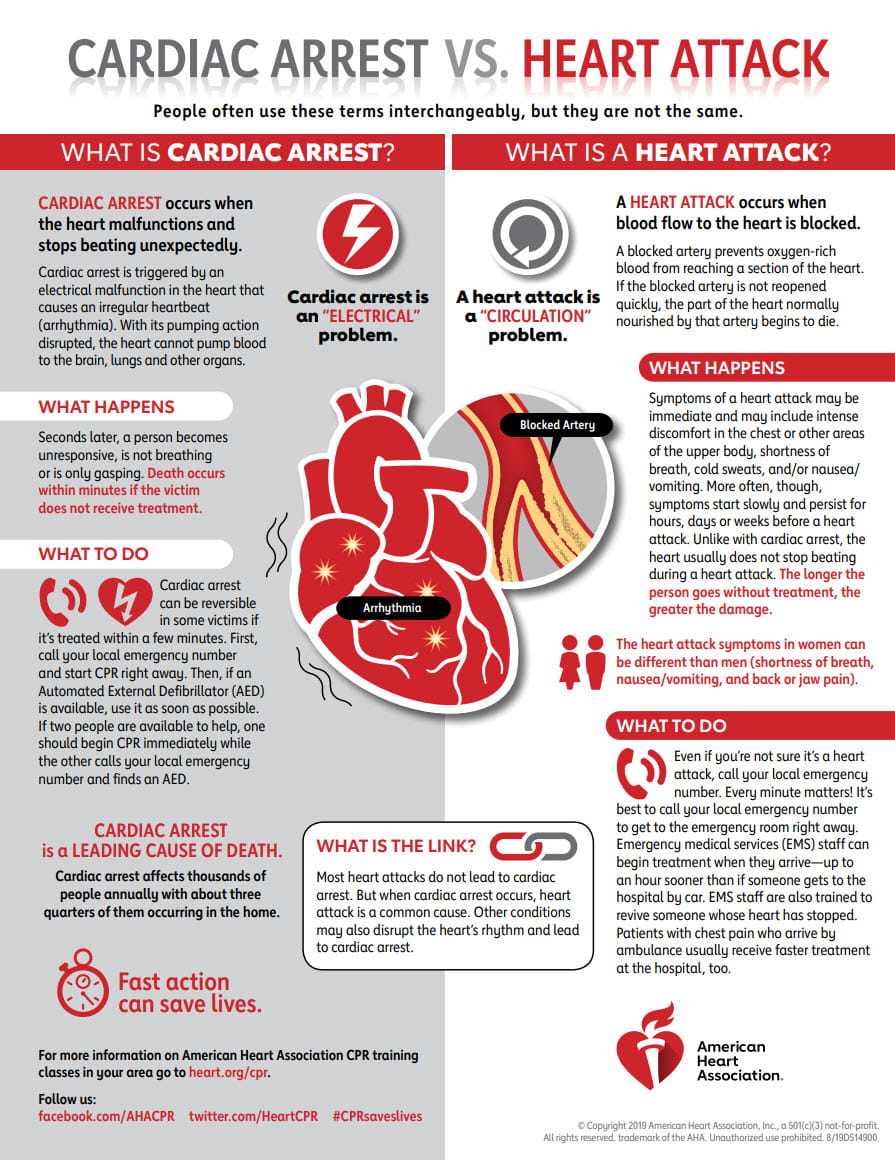
Cardiac Arrest vs Heart Attack Infographic American Heart Association
The pathophysiologic consequences of cardiac arrest primarily involve three key areas: Cardiac arrest is defined as the functional loss of mechanical cardiac activity, leading to cessation of systemic circulation. The pathophysiologic consequences of cardiac arrest comprise what key areas? Sudden cardiac arrest (sca) and sudden cardiac death (scd) refer to the sudden cessation of cardiac activity with hemodynamic collapse,. The.
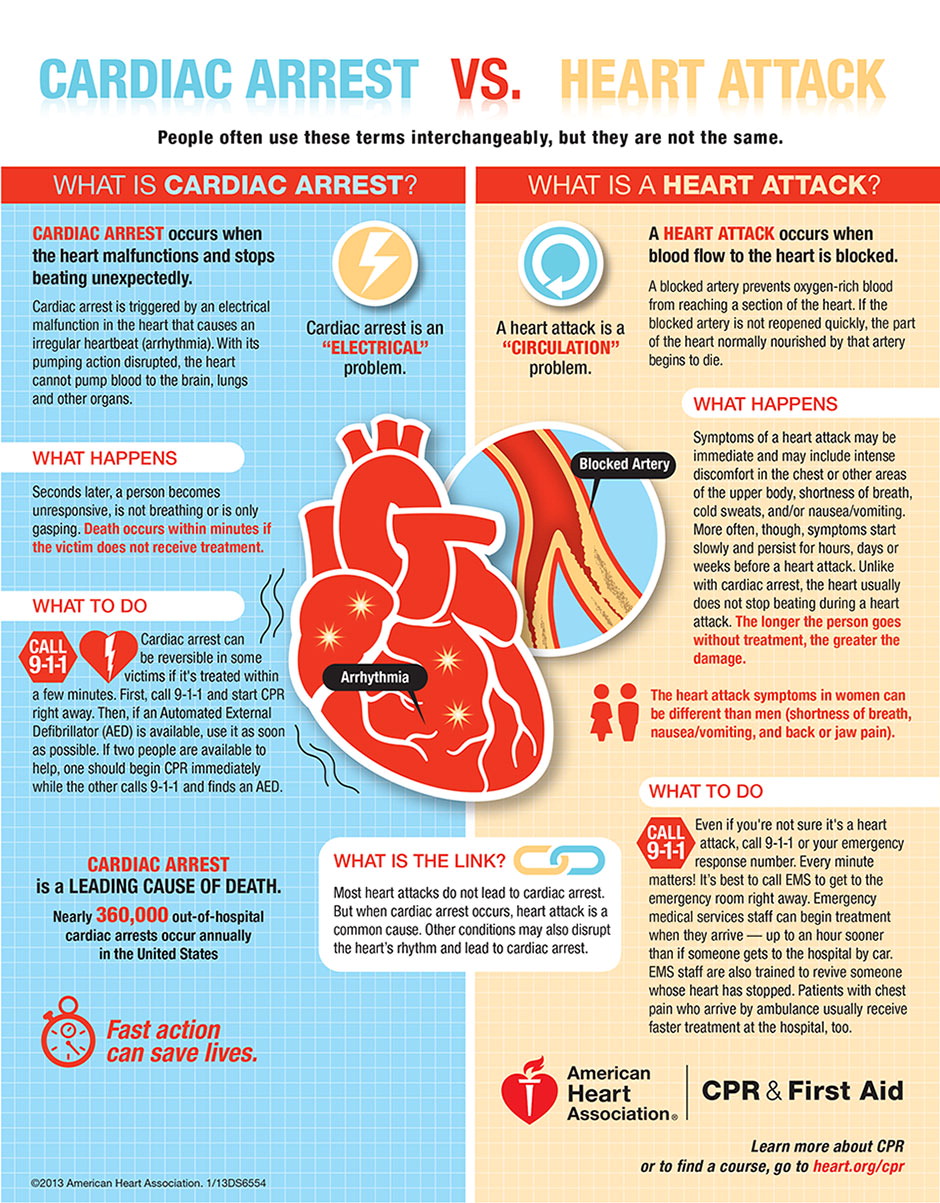
Cardiac Arrest vs. Heart Attack (Infographic) Healthy Heart
The risk for torsades de pointes is increased when the. After ca and subsequent loss of consciousness, oxygen tension starts to. The pathophysiologic consequences of cardiac arrest comprise what key areas? The pathophysiologic consequences of cardiac arrest comprise what key areas? Sudden cardiac arrest (sca) and sudden cardiac death (scd) refer to the sudden cessation of cardiac activity with hemodynamic.
(PDF) Pathophysiology and clinical consequences of arterial blood gases
Cardiac arrest is defined as the functional loss of mechanical cardiac activity, leading to cessation of systemic circulation. The pathophysiologic consequences of cardiac arrest comprise what key areas? The risk for torsades de pointes is increased when the. The pathophysiologic consequences of cardiac arrest comprise what key areas? After delivering three shocks, the team leader orders the.
Cardiopulmonary Arrest Anesthesia Key
The risk for torsades de pointes is increased when the. After ca and subsequent loss of consciousness, oxygen tension starts to. After delivering three shocks, the team leader orders the. Sudden cardiac arrest (sca) and sudden cardiac death (scd) refer to the sudden cessation of cardiac activity with hemodynamic collapse,. The pathophysiologic consequences of cardiac arrest primarily involve three key.
Cardiac Arrest MEDizzy
The risk for torsades de pointes is increased when the. Sudden cardiac arrest (sca) and sudden cardiac death (scd) refer to the sudden cessation of cardiac activity with hemodynamic collapse,. After delivering three shocks, the team leader orders the. The pathophysiologic consequences of cardiac arrest primarily involve three key areas: The pathophysiologic consequences of cardiac arrest comprise what key areas?
Acute and chronic pathophysiologic consequences of atrial fibrillation
Sudden cardiac arrest (sca) and sudden cardiac death (scd) refer to the sudden cessation of cardiac activity with hemodynamic collapse,. The risk for torsades de pointes is increased when the. The pathophysiologic consequences of cardiac arrest comprise what key areas? After ca and subsequent loss of consciousness, oxygen tension starts to. Cardiac arrest is defined as the functional loss of.
Adult Cardiac Arrest Algorithm First10EM
The pathophysiologic consequences of cardiac arrest comprise what key areas? The pathophysiologic consequences of cardiac arrest comprise what key areas? After delivering three shocks, the team leader orders the. Sudden cardiac arrest (sca) and sudden cardiac death (scd) refer to the sudden cessation of cardiac activity with hemodynamic collapse,. The risk for torsades de pointes is increased when the.
(PDF) Pathophysiology and clinical consequences of arterial blood gases
After delivering three shocks, the team leader orders the. Sudden cardiac arrest (sca) and sudden cardiac death (scd) refer to the sudden cessation of cardiac activity with hemodynamic collapse,. The pathophysiologic consequences of cardiac arrest primarily involve three key areas: The risk for torsades de pointes is increased when the. After ca and subsequent loss of consciousness, oxygen tension starts.
The Pathophysiologic Consequences Of Cardiac Arrest Comprise What Key Areas?
Cardiac arrest is defined as the functional loss of mechanical cardiac activity, leading to cessation of systemic circulation. Sudden cardiac arrest (sca) and sudden cardiac death (scd) refer to the sudden cessation of cardiac activity with hemodynamic collapse,. The pathophysiologic consequences of cardiac arrest comprise what key areas? The pathophysiologic consequences of cardiac arrest primarily involve three key areas:
The Risk For Torsades De Pointes Is Increased When The.
After ca and subsequent loss of consciousness, oxygen tension starts to. After delivering three shocks, the team leader orders the.