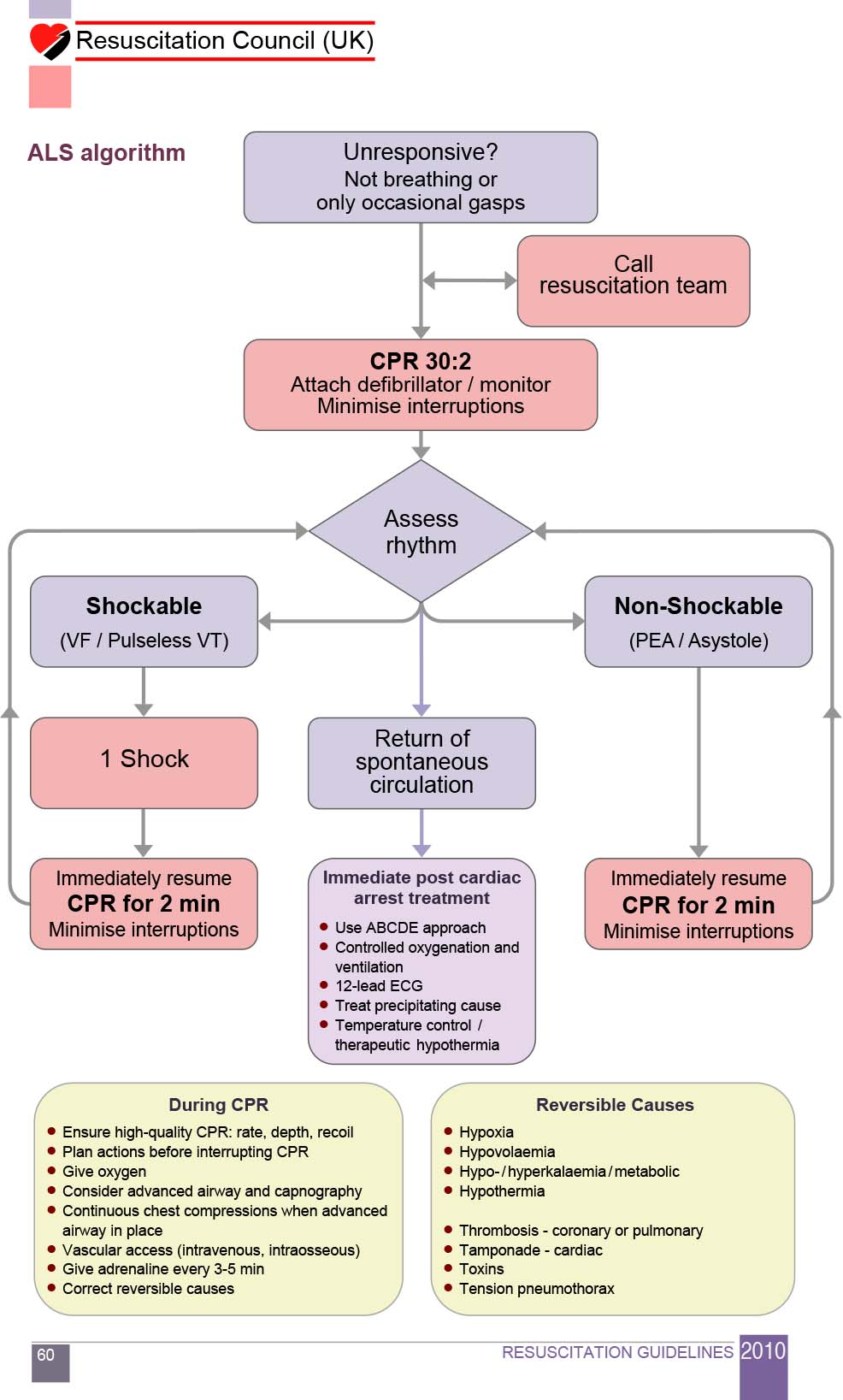
Dose Of Sodium Bicarbonate In Cardiac Arrest - Base subsequent doses on results of arterial blood ph and paco2 as well as calculation of base deficit. Sodium bicarbonate should only be used after establishment of airway and adequate ventilation.(5,6) routine use of sodium. Sodium bicarbonate (sb) administration has been considered an important part of treatment for severe metabolic acidosis in cardiac arrest,. In cardiac arrest, a rapid intravenous dose of one to two 50 ml vials (44.6 to 100 meq) may be given initially and continued at a rate of 50 ml (44.6.
Sodium bicarbonate (sb) administration has been considered an important part of treatment for severe metabolic acidosis in cardiac arrest,. Sodium bicarbonate should only be used after establishment of airway and adequate ventilation.(5,6) routine use of sodium. Base subsequent doses on results of arterial blood ph and paco2 as well as calculation of base deficit. In cardiac arrest, a rapid intravenous dose of one to two 50 ml vials (44.6 to 100 meq) may be given initially and continued at a rate of 50 ml (44.6.
In cardiac arrest, a rapid intravenous dose of one to two 50 ml vials (44.6 to 100 meq) may be given initially and continued at a rate of 50 ml (44.6. Base subsequent doses on results of arterial blood ph and paco2 as well as calculation of base deficit. Sodium bicarbonate should only be used after establishment of airway and adequate ventilation.(5,6) routine use of sodium. Sodium bicarbonate (sb) administration has been considered an important part of treatment for severe metabolic acidosis in cardiac arrest,.
Cardiac Arrest Oxford Medical Education
Sodium bicarbonate (sb) administration has been considered an important part of treatment for severe metabolic acidosis in cardiac arrest,. Sodium bicarbonate should only be used after establishment of airway and adequate ventilation.(5,6) routine use of sodium. In cardiac arrest, a rapid intravenous dose of one to two 50 ml vials (44.6 to 100 meq) may be given initially and continued.
Use of sodium bicarbonate in outofhospital cardiac arrest a
Base subsequent doses on results of arterial blood ph and paco2 as well as calculation of base deficit. In cardiac arrest, a rapid intravenous dose of one to two 50 ml vials (44.6 to 100 meq) may be given initially and continued at a rate of 50 ml (44.6. Sodium bicarbonate should only be used after establishment of airway and.
Sodium Bicarb in Cardiac Arrest EMRA
Base subsequent doses on results of arterial blood ph and paco2 as well as calculation of base deficit. Sodium bicarbonate (sb) administration has been considered an important part of treatment for severe metabolic acidosis in cardiac arrest,. In cardiac arrest, a rapid intravenous dose of one to two 50 ml vials (44.6 to 100 meq) may be given initially and.
Prove It Is sodium bicarbonate indicated for prolonged cardiac arrest?
In cardiac arrest, a rapid intravenous dose of one to two 50 ml vials (44.6 to 100 meq) may be given initially and continued at a rate of 50 ml (44.6. Sodium bicarbonate (sb) administration has been considered an important part of treatment for severe metabolic acidosis in cardiac arrest,. Sodium bicarbonate should only be used after establishment of airway.
Sodium Bicarbonate FDA prescribing information, side effects and uses
Sodium bicarbonate should only be used after establishment of airway and adequate ventilation.(5,6) routine use of sodium. In cardiac arrest, a rapid intravenous dose of one to two 50 ml vials (44.6 to 100 meq) may be given initially and continued at a rate of 50 ml (44.6. Base subsequent doses on results of arterial blood ph and paco2 as.
Sodium Bicarbonate Package Insert / Prescribing Information
Base subsequent doses on results of arterial blood ph and paco2 as well as calculation of base deficit. Sodium bicarbonate should only be used after establishment of airway and adequate ventilation.(5,6) routine use of sodium. In cardiac arrest, a rapid intravenous dose of one to two 50 ml vials (44.6 to 100 meq) may be given initially and continued at.
Sodium Bicarbonate Injection, USP
In cardiac arrest, a rapid intravenous dose of one to two 50 ml vials (44.6 to 100 meq) may be given initially and continued at a rate of 50 ml (44.6. Base subsequent doses on results of arterial blood ph and paco2 as well as calculation of base deficit. Sodium bicarbonate (sb) administration has been considered an important part of.
Use of Sodium Bicarbonate During Pediatric Cardiac Admissions with
In cardiac arrest, a rapid intravenous dose of one to two 50 ml vials (44.6 to 100 meq) may be given initially and continued at a rate of 50 ml (44.6. Base subsequent doses on results of arterial blood ph and paco2 as well as calculation of base deficit. Sodium bicarbonate should only be used after establishment of airway and.
Hospira recalls sodium bicarbonate vials as the drug shortage gets
Sodium bicarbonate should only be used after establishment of airway and adequate ventilation.(5,6) routine use of sodium. In cardiac arrest, a rapid intravenous dose of one to two 50 ml vials (44.6 to 100 meq) may be given initially and continued at a rate of 50 ml (44.6. Sodium bicarbonate (sb) administration has been considered an important part of treatment.
Sodium Bicarbonate FDA prescribing information, side effects and uses
In cardiac arrest, a rapid intravenous dose of one to two 50 ml vials (44.6 to 100 meq) may be given initially and continued at a rate of 50 ml (44.6. Sodium bicarbonate (sb) administration has been considered an important part of treatment for severe metabolic acidosis in cardiac arrest,. Base subsequent doses on results of arterial blood ph and.
Sodium Bicarbonate Should Only Be Used After Establishment Of Airway And Adequate Ventilation.(5,6) Routine Use Of Sodium.
Base subsequent doses on results of arterial blood ph and paco2 as well as calculation of base deficit. In cardiac arrest, a rapid intravenous dose of one to two 50 ml vials (44.6 to 100 meq) may be given initially and continued at a rate of 50 ml (44.6. Sodium bicarbonate (sb) administration has been considered an important part of treatment for severe metabolic acidosis in cardiac arrest,.